Introduction
In order to define business strategy, it is a long-term plan. In which a company designed goals and visions to achieve success and to get better outcomes. Business strategy of Vodafone company is influenced by environmental factors such as micro factors or macro factors. There are too many factors who influenced the organisational strategic position. Vodafone is using Ansoff’s growth vector matrix and VRIO/VRIN model to analyse strengths and weaknesses and capabilities. For environmental analysis, company is using PESTLE analysis, which is known as one of the best strategy in telecommunications sector.
Increase Your Odds of Success With Our
- Scholastic academic documents
- Pocket friendly prices
- Assured reliability, authenticity & excellence
P1 Impact and influence of macro environment on Vodafone organisation and business strategies
Vodafone is a world's best multinational telecommunication company. Vodafone was found in 1991. This is public limited telecom company and head office of Vodafone is established in UK. There are many types of macro environmental factors which influenced the organisational structure of Vodafone company. Macro environmental factors such as demographic, economic, natural, technological, political and cultural. PESTEL analysis is one of the best way to define macro environmental factors.
Explanation of PESTEL analysis:
- POLITICAL: Political factor can affect the business in many ways. These factors can be explained as tax policy, health and safety law, import restriction on quantity and quality of product, employment law and economy. Vodafone company has to be identify these political factors because changes in political factors can affect the organisation directly or indirectly.
- ECONOMIC: Economic factors play a vital part in decision making process of any organization. When Vodafone is making financial decision, then it should be considered by this company. Economic factors such as interest rates, taxes rate, exchange rates and demand or supply. Vodafone is related to the economy in a vital part.
- SOCIAL: Vodafone should consider the social aspects, when making of business strategies. Because as we all know that society is continuously changing. Fashion and taste of customers are main factors in making strategies. If Vodafone wants to achieve better outcomes, then it is necessary to find out all social factors.
- TECHNOLOGICAL: these are those factors who affect indirectly on business strategies of any organisation (Welford, 2018). Factors of technology such as automation, engine efficiency, internet and 3D technology. Vodafone company is majorly affected by these factors.
- ENVIRONMENTAL: climate changes, weather and pollution are the factors of environment. These can also impact the business strategies and influences the organisation in many ways.
- LEGAL: these factors are external factors. All organisations are bounded in legal framework. All companies have to follow all regulations and rules. If Vodafone wants to make changes in prices of their products, then it should follow the legal factors. Without this, they cannot make any changes in prices.
To analyse the organisation’s strategic positioning by Ansoff’s growth vector matrix:
This matrix helps management team to focus on the options which can be useful in business growth. This matrix is built around two factors such as
- new products and current products
- new markets and current markets
In this matrix, there are four types of strategies applicable such as market penetration strategy, market development strategy, diversification and product development strategy (Welford, 2018). Ansoff's growth vector matrix can be defined by this diagram:
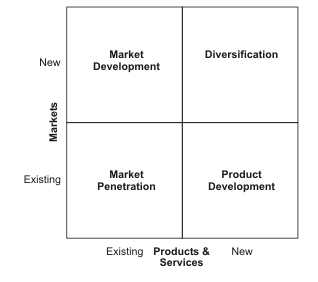
Vodafone company is required to focus on these four factors to grow business. If Vodafone is using market penetration strategy than it would be better to focus on existing customers and in product development, company has to be develop innovative ideas and creativity related to design in their products. This strategy can be used as a tool to identify options related to business growth. It can help in to identify the opportunities but it cannot help to evaluate which opportunity is worth pursuing and which is not. It also helps in to evaluate SWOT analysis. Some opportunities can be rejected quickly but it is necessary to focused and deep look into factors. To do market penetration, Vodafone needs to find out all new ways to grow consumer loyalty and lifetime values. Market development is a strategy to attract new consumers for their existing product. New customers mean may be form different location as geographic or demographic. Diversification is a strategy in which a company is selling new products in new markets. This matrix helps in to identify the location which is suitable for selling products.
M1 Critically analysis of macro environment and analysis how it affects the business strategic decisions:
When Vodafone company makes business strategies, then it should be considered all the factors of macro environment. Because without concentrate on factors like environment and legal, company cannot achieve success. Business strategies are long term vision process, which cannot be change again and again but environmental factors are continuously changing, hence it is necessary to find out information about all the factors. As example: Vodafone is going to launch a new phone, they made business strategies related to launch the product without knowing about all factors (Shimizu and Tamura, 2015.). At the last, company will not achieve success. Because company did not know customers taste and preferences. They made strategies on the basis of past records but these are the environmental factors which are continuously changing. So, it is necessary for all the organization to analyse all the factors of macro environment.
P2 Internal environment and capabilities of Vodafone organisation:
The stage of a company will be based on the internal capabilities of a company. There are six stages in value chain of Vodafone:
- technology development
- product design
- manufacturing
- marketing
- distribution
- service
Technology development: Vodafone gives a lot of importance on technology development because by using of this factor company achieved economies of scale. This is replicated in all operations. As we know that it will be cheaper operations by sharing fixed costs. To get economies of scale, there is required to setting up a service centre (Shimizu and Tamura, 2015.).
Product design: this is linked to first factor because Vodafone's products are based on technology. Company has to be assure that they include all the characteristics and qualities of a product.
Manufacturing: this is closely linked to Vodafone's chain of supply. Economies of scale can be achieved through this process. Integration, assembly, procurement, capacity and parts production are the aspects of manufacturing chain.
And the last is distribution and services. Value chain of Vodafone is composed by nine generic activities and all the factors are linked together. These 9 generic activities can be divided into two main parts such as: primary or support. Physical creations of the product, after sales services and sale of the product will be included in primary activities. The second activity is supportive activity who helps to the primary activities by providing various information and human resources. Manufacturing and marketing activities can be divided into sub activities to achieve competitive advantages. All the factors must be involved in both of the categories.
value chain is the tool, which is useful to design all the activities of the organisation. It is also used to compare and analyse the costs. There are three important process to perform value chain:
- Identify
- analysis
- decide
Identify: in this process, Vodafone has to be identify all the macro activities, main activities and those activities which brings value to consumers in the business.
Analysis: in this process, Vodafone has to analyse main cost drivers, strength and weaknesses and areas which has to be improved.
Decide: Vodafone has to decide that which activity or strategy is suitable for their organisation. It is required to maintain competitive advantages.
Determination of strategic capabilities by VRIO/VRIN model
VRIO model is a tool which is used by an organization to analyse the internal resources and capabilities to find out competitive advantages. For using this tool, company has to follow this process:
- To identify valuable and costly resources
- Find out the organised form
- Protect the resources
- continuously review VRIO resources
Evaluation of Vodafone's capability through VRIO model:
|
Vodafone's VRIO capability |
|
Valuable? |
Rare? |
costly |
Company organized to exploit? |
|
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
|
Result: good strategic capabilities |
Strengths and weaknesses of Vodafone:
strength:
- its market coverage: Vodafone's market coverage area is too broad. It's known for broad network area and broad distribution channel. Vodafone operates in almost 25 countries across the world.
- income generated: Because of the wide coverage areas, revenue of the company is continuously increasing.
- marketing strategy: Vodafone comes out in a market with new strategies. By these new strategies, company gathered millions of customers.
- premium cost: while other companies are using penetrating marketing strategy, but Vodafone is using differentiation marketing strategy. Hence, company is maintaining its positive margins (Leonidou and et.al., 2017.).
- brand valuation: brand valuation of Vodafone is too high, no one can match this level. Rather than brand evaluation, brand recall and brand equity is also very high.
- subscriber base
weakness:
- dropping subscriber base: this is a main and major weakness of Vodafone. From last 4 years, company is dropping its subscriber base.
- dropping brand valuation: the main reason for dropping subscriber base is dropping brand valuation. If Vodafone wants to become the strongest company in the world, then these both points are also to be considered (Jamasb, Thakur. and Bag, 2018).
- decrease market share: the market share of Vodafone company is also dropping fast. The main float source of this company is USA. But from last 2 to 3 years, it is losing its market share.
- poor performance: due to economic conditions, Vodafone's performance level is decreasing fast.
M2 The strengths and weaknesses of Vodafone's structure and skill set :
strengths are
- specialization
- productivity
- functional structure
- product based structure
- customer based structure
- business process team
weaknesses are:
- management issues
- unit coordination
- communication skills
- interpersonal skills
Strengths are internal factors of a company which is in controlled. Strengths of Vodafone company on the basis of organisational structure and skill set can be classified as financial resources, intellectual property, human resources and physical items (Leonidou and et.al., 2017.). Weaknesses are also internal factors which can be controlled by an organisation. Weaknesses of Vodafone company on the basis of skill set and organisational structure can be classified as cut-throat competition and absence of profitability.
P3. Evaluate the competitiveness of telecommunication sectors of UK using Porter's Five Model.
Task 3
P3. Evaluate the competitiveness of telecommunication sectors of UK using Porter's Five Model.
Porter's Five Model determine five forces which analysis the competitive position and strength of a business. It is a framework which determines the competitive intensity and attractiveness of market. Every telecommunication company in UK uses Porter's Five Model because of the competitive position and strength of business is influenced by the five forces of the model.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Porter's five forces of buyer refers to the pressure exert on Vodafone telecom business to get them available of high quality, better customer services and lower services. According to the Porter's five Model- buyer power is one of the forces that shapes the competitive structure of Vodafone Company. Vodafone buyers are in numerous subscriber’s but still the bargaining powers of buyer of Vodafone is strong as because of competition in the market. The customers of Vodafone are powerful which reduces the cost of services and products. These buyers cut down the leader monetary value but not past the level of rivals. To control the bargaining powers of Vodafone buyer, it should ensure the returns above the competitors in the telecommunication sectors. Company is using this porter's model which analysis the competition prevailing in the market which influenced the prices, quality of services and products of company. Sometimes, Buyers also bargains for enhancing the services of products in same rate before.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers of telecommunication sectors is quite considerable than compare to other sectors. However, Vodafone suppliers have high bargaining power since company operates in great perimeter comparing to another telecom company. The products of Vodafone company like broadband, SIM, mobile handset, fibre optical cables etc. Company would not able to do its job but there are numerous makers around the market. There are enough vendors which dilute the bargaining powers of suppliers. Vodafone easily maintains the bargaining powers of its suppliers by lowering its price and making continuous profits. Porter’s five forces analysis that the firm is affected by increasing the prices and reducing the quality of services and products. In UK the bargaining powers of telecom company is quite low as the availability of many suppliers, less diversity and low switching cost.
- c) Threats of new entrants
Vodafone Company faces appreciable threat to its products and services. Still Vodafone does not have to lower down its prices due to impressive economic scale and muscular power of buyers. Moreover, finance is also become biggest barriers of entry as telecommunication sector require huge cost and typically require heavy cash in hand to start up the business. In UK, a telecommunication company has to apply for the license Federal Communication Commission (FCC) for approval to start their business. Vodafone has adorable skills of management which also making difficult for new entrants. Vodafone is maintaining its long chain of distributions which is not easy for any other new entrant to cope up because of cost of distribution is very high. The cost of setting up of infrastructure for a telecommunication company is very high which also have barriers. There is rapid change in technology in telecom sector which also require cash.
Threats of Substitutes
Vodafone faces respectable substitutes of products and services. The CDMA services and basic landline phones are declining with the innovation of Broadband services which are becoming ordinary. Social networking sites like Face book, Instagram and other services like Video calls, emails, yahoo, Skype and many other services have taken place as substitute of mobile services. Vodafone does not need to pass down the cost of submission due to strong and powerful and effective scale of management. The services provided by Vodafone is admired by the buyers of company, which can be seen by the coverage of market share in the telecom sector.
Rivalry within the market
Competition is cut thought in telecom Sector. Vodafone is fighting intense competition from its rivalry due to low cost charged by the competitors. The price charged by the competitors, it has to be provided by the Vodafone Company because switching cost is high in a telecommunication company. At every step there are high competition. Increasing price with increasing quality is not important for buyer, they also note the prises other company is offering to them. New technology is prompting a deal of substitute services.
M3. Devise strategies to improve the competitive edge and market position of Vodafone
Vodafone company make strategies to improve its competitive edge and market position making efforts to sustain the buyers by fulfilling their expectations and by introducing smart and advance technologies than other company, and by controlling the bargaining powers of suppliers by making relationship with numerous suppliers.
P4 Using Bowman Strategies of clock Model, Analysis the strategic direction and option available to Vodafone
Bowman Strategies of Model is a framework used by the telecommunication companies for designing marketing strategies to analysis the competition in the market and analysing the competitive position of company. Bowman Model has eight competitive direction for edge. Bowman strategies Model is basically based on the Porter's theory but it is the expansion of porter's five forces into eight forces.
Low price/ low added value (Position1)
This is a segment particular option and Vodafone does not choose to complete this category, generally companies in telecommunication sector does not choose to complete this because of competition in the market and high switching cost. When the product of company is lack differentiated value than company us this position. Vodafone being the market leader in telecommunication company, they have to keep their prices of products very less with added value services and keep main focus on customers.
Low Price (Position2)
For attracting customer company use this position as keeping the price very low. Vodafone when introducing the new products or services pleading low price which attract the consumers to subscribe. In this position the main focus is on attract of consumer having lowest price. Mainly in this position company try on focussing on under-cutting competitors via lowering cost of the product or services. Pushing down of prices results fall in margin. Companies are becoming leader in low price using this position of Bowman Model.
Hybrid (postion2)
This position includes low price and some differentiation in products and services. They produce lower cost products and services and also offer some product specialization. Many small-scale businesses fall into this position because they cannot compete with large businesses. In this position more focus is on manufacturing goods dependable products and services at reasonable and fair price (Owusu and Duah, 2018). In this position of Bowman Model loyalty to succeed and customer convenience is achieved.
Differentiation (position4)
For creating unique position in the marketplace, differentiating the product and services is must be present in the company. Vodafone has unique position in the marketplace by differentiating its product and services. When company introduce unique product or services in the market, the profit margin is at peak level. Higher profit is gain by the company when product and services is differentiated from competitors. Companies in this position of Bowman Model focussed mainly on differentiation of products. The unique aspect creates a higher value of offers for a higher price on the product or services and achieve targeted sales. Branding play key role in differentiation of products (Shamsuzzaman and et.al, 2018.).
Focused Differentiation (position5)
As the same position4. Differentiation concerns the unique attributes of product and services. In comparison to competitors in the marketplace. In this position the market segment is targeted, according to the proposition value. If it is higher, the price of product is also higher. In this position it is not necessary that product have any intrinsic value but the perception of value by the customer is enough (Naor, Druehl and Bernardes, 2018).
Increased price (position6)
Many companies take advantages of market supply disequilibrium and approach short term strategies and increase the price of the products. Companies producing differentiated and innovative products apply increase price. If the increased price is accepted by consumers, company enjoy high profit in the marketplace, and if it not accepted by customers than it is very bad for company, as its market share fall, and it keep on falling if company make adjustment in price level.
High price/ low price (position7)
This position belongs to the company who has monopoly in the market. Company have no concern about adding value in their product and services because they know very-well that where will customer move. There is no substitute available in the market. Customer will definitely pay for its product and services. But in today's world new companies are coming very soon with innovated products, so monopolist don't have so much long time to remain as monopolist in the market. Companies having intellectual property rights fall in this position of Bowman Model.
Low Value/ Standard Price (position8)
Company loss its market share surely if company pursues this market strategy. If the product is old or outdated, it can solve only at low price. Company having low value product cannot be sell at standard price. Short term and trend markets are affected by this strategy. This strategy will alienate the customers and market share will be lose. This strategy involves the inferior products and pricing it to match the price of substitute products which are not outdated.
M4. producing a strategies management plan that has tangible and tactical strategic priorities and objectives
For healthy business innovation is a cornerstone. Company should not work only on existing business but promote the business by making strategic plans which increases its market share and maintain it. Retain, maintain, expand educate and invest is the main factors that helps in achieving goals of business.
Set in Motion the Plan for Exemplary Grades with Our Extensive Academic Writing Services
Premium Assignment Services
Conclusion
The above report concluded that business strategies are very important for each and every organisation. Effective strategies help in gaining competitive advantages in a market as well as support in improving performance as well as profitability. The report identified various external and internal factors which are affecting business functions and strategic planning in Telecommunication Sector. The report included various analysis tools such as Bowman Strategies of clock Model and Porter's Five Forces. In order to identify the factors affecting business operations of Vodafone. Furthermore, the report also determined various strategies that can be adopted by the organization in order to gain competitive advantages and sustain a leading position in the telecommunication industry. Furthermore, the assessment giving direction to Vodafone Company how bargaining power of buyer and suppliers can be controlled and how the porters-five-forces can be implemented in the organisation. This report also helps in fixing the price level of products and services. Visit Instant Assignment Help for more help with assignment.
You may also like to read: Unit 1 Global Business Environment Pearson BTEC Level 5
References
- Buckley, P. J., Burton, F. and Mirza, H. eds., 2016.The strategy and organization of international business. Springer.
- Jamasb, T., Thakur, T. and Bag, B., 2018. Smart electricity distribution networks, business models, and application for developing countries. Energy Policy. 114. pp.22-29.
- Leonidou and et.al., 2017. Internal drivers and performance consequences of small firm green business strategy: The moderating role of external forces.Journal of business ethics,140(3), pp.585-606.
- Naor, M., Druehl, C. and Bernardes, E.S., 2018. Servitized business model innovation for sustainable transportation: Case study of failure to bridge the design-implementation gap. Journal of Cleaner Production. 170. pp.1219-1230.
- Owusu, P.A. and Duah, H.K., 2018. Evaluating total quality management as a competitive advantage tool in mobile telecommunication services in Ghana. European Journal of Research and Reflection in Management Sciences Vol. 6(1).
- Parnell, J.A., 2016. A business strategy typology for the new economy: reconceptualization and synthesis.Journal of Behavioral and Applied Management,3(3).
- Shamsuzzaman, M. and et.al, 2018. Using Lean Six Sigma to improve mobile order fulfilment process in a telecom service sector. Production Planning & Control. pp.1-14.
- Shimizu, N. and Tamura, A., 2015. The Effects of Business Strategy on Economic Evaluation Techniques of Capital Investment.
- Welford, R., 2018. The launch of a new journal, Business Strategy and Development.Business Strategy & Development,1(1), pp.4-5.












