Introduction
Any business organisation has to ensure the survival of it depending upon the extent and quantity of sales that it can achieve in the market. Sales management is the ultimate process of business profit maximisation that determines the measure of income any corporate organisation can generate from the existing market by launching the goods and services that such organisations could offer as products. The following thesis study enumerates the various innate features and the consequent importance of sales management of a selected organisation and explores the various aspects which influence the growth and maintenance of such activities associated with sales and marketing of produced goods.
Increase Your Odds of Success With Our
- Scholastic academic documents
- Pocket friendly prices
- Assured reliability, authenticity & excellence
Task 1: Understand the role of personal selling within the overall marketing strategy
1.1 Explanation of the way personal selling supports the promotion mix
Personal selling: Such methods of selling goods and products are achieved through the exchange of information through the mode of oral communication with potential buyers of any product. The driving force behind such interaction is the intention of performing a successful sale to a buyer by the sales person. The methods of personal selling have to focus initially on the development of the relationship based on trust with the potential buyers. The ultimate objective of the relationship development is always being the successful conclusion of persuading the potential buyer into accepting the product under consideration on the terms and conditions offered by the salesperson (Kotleret al.2015, p.122). This climax of the sales process is known as closing the sales exercise. Any prospect of success of such sales operations depends on the in depth understanding of the behavioural preferences of the consumers on part of the sales person. The necessities and choices of products of the targeted customer base ultimately become the determinant of the outcome of any sales operation. The relevance and importance of personal sales management could be understood from the fact that such forms of personal selling of goods and products contribute in convincing the customer to come to terms with the product offering on a much greater scale than that of indirect or bulk selling. The impact of personal engagement of the sales personnel in selling of goods and products is always a positive one on the selected customers (Hulthén et al. 2016, p.820). The new cosmetics product line of L’Oréal is yet to be introduced into the market and this explains the lack of exposure that the potential customers have with such upcoming product offerings. The personal approach in marketing of the prospectus products and in building the base of brand loyalty and trust in the existing and impressionable potential customers is thus of paramount importance to ultimately promote the products further into the market segments (Boone and Kurtz, 2013, p.147).
Promotion mix:Every process mix, undertaken to achieve any specific purpose consists of a series of associated, relevant and interdependent activities. The primary element in the introduction of the product specifications to the potential customers is the marketing tool of advertisement. Effective advertising strategy makes the processes of direct marketing and personal sales of goods and products successful (Lee et al.2016, p.140). In case of L’Oréal, the new cosmetic brands that the company is launching into the market require the basis of powerful public relations exercises to generate greater focus of attention by the potential consumers on such line of new products. The elements of any promotional process mix are always necessitated to operate in integration and in tandem with each other and the measure of success automatically promote sales (Stone and Woodcock, 2014, p.10).
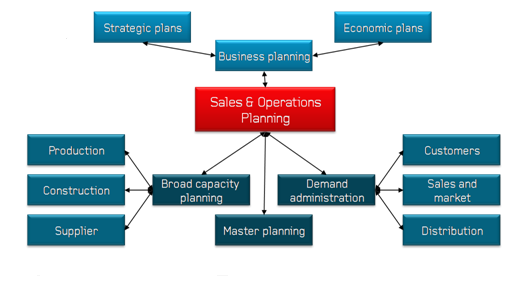
Figure1: Planning mechanism for operations and sales
(Source: Thoméet al. 2012, p.7)
1.2 Compare buyer behaviour and the decision making process in different situations
Consumers are the end users of any product or service and it is of utmost importance to determine the pattern of behaviour that individual and groups of customers exhibit in selecting products and services from the market. Consumer behaviour could be thus defined as the process of decision making on part of the consumer in terms of purchase behaviour (Armstronget al. 2014, p.130).
Behaviour of the consumer:The study of the behavioural aspects of purchase and selection preference on part of the consumers is of crucial importance for any sales promotion exercise of any corporate entity to succeed in the marketing of the goods and products. Study of the behaviour of the consumers require the blending of various scientific disciplines such as psychology, social anthropology, sociology, market management and economic analysis of the prevalent financial conditions with the objective to successfully deduce the internal factors that influence the decision making process of the consumers and the buyers (Solomon et al.2013, p.126). Consumer behaviour identification includes the analysis and evaluation of the various characteristics of individual consumers such as the features of the demographic and behavioural variables associated with it. Such aspects assist any organisation in understanding the stated and the unstated necessities of the people at any given time. Consumer behavioural studies attempt to assess the group influence of family, friends and the society in general on the consumer preferences. It also includes the study of diverse circumstantial factors such as the age groups, gender, race, cultural backgrounds and religious lineages (John, 2015, p.15).
Any decision making process is the sum total of the different emotive, practical and psychological consideration of the customers. The consumers change their decisions regarding product preferences depending on the influence of the prevalent situation in the society (Schiffmanet al.2013, p.149).
Over the course of the development of the markets in the postmodern age, a gradual transformation of the market perspective has taken place where previously the orientation of the market activities was to serve that of the sales process and now the core constituent of any successful business operation is to meet the expectations of the buyers. The product promotion planning process thus requires the concentration of all the resources of any business organisation such as the L’Oréal, on to the acquisition of the understanding of customer preferences and decision making procedure regarding the variations of choices of products (Jobber and Lancaster, 2012, p.120).
Various external influences and stimuli contribute in shaping the customer preferences and choice mechanisms. Consumers are often persuaded by logical arguments during the purchase of essential amenities and in some cases the consumer behaviour expresses marked influence by emotive factors where luxury goods are concerned such as the cosmetic product line offered by the L’Oréal. The obtainment of understanding of such factors assists the companies to formulate product development and promotional strategies (Tanner et al.2013, p.131).
Types of Personal Selling: Inside order-taker:This method is associated with the retail sales performance. The customer makes the choice in this case and the responsibility of the sales assistant is only to perform the financial transaction by the reception of payment and supplying the goods and the products selected by the customer (East et al.2013, p.128).Telemarketing sales processes are also including in the order taking format of marketing as such services cater to the bulk sales efforts of any company at any region.
Delivery sales:Such form of sales management is primarily concerned with delivering products and goods. The proficiency of the services is dependent on the changes in order sizes and such mechanisms are purely driven by customer preferences (Lassk et al. 2012, p.149).
Outside order-taker sales personnel:Such sales people do not deliver any substance but they respond to customer requirements and visit the customer premises to provide necessary information relating to products and services.
1.3 Analysis of the role of sales teams within marketing strategy
Market segment identification and promotion of the product brand: Marketing involves the identification of market segments primarily. Such identification of the probable regions and customer bases that could be utilised to perform better sales of the offered products depends on the considerations of product development cost, pricing structure and promotional techniques. The responsibilities of the sales and marketing teams is to provide emphasis on the market research, determination of customer profiles, planning of distribution strategies and highlighting brand management among the potential customers. After such objectives are achieved, the sales and marketing teams create effective market communications through advertisements, public relations exercises such as trade fairs and through the social media utilisation (Turnbull and Valla, 2013. p.141)
Strategy: Once sales and marketing team members know which market segment they represent, they have to make sure that the team marketing strategy addresses the needs of their segment. Each team member is responsible for sales in her area, and the common strategy has to include facets that address any particular needs. If an industrial segment has an essential feature that only it needs, for example, the promotional material targeting that segment has to highlight the essential feature. The role of a team member in developing marketing strategy is that of advocate for the needs of the target market for which he is responsible (Ingramet al.2012, p.134).
Marketing plan implementation: Each team member in a sales and marketing team becomes responsible for implementation of marketing plans after the strategy of product promotion could be developed. These responsibilities include determining the promotional material the market segment and specifications of the pricing structures. Sales managers put on the mantle of responsibility for developing sales targets and objectives (Kapferer, 2012, p.139).
A cohesive and team handles carefully the juxtaposing demands of sales and marketing environment to achieve the specified business objectives. In this process, each member becomes the responsible person to not only perform the individual duties of him/her but to lend the services of him/her in fulfilling the group objectives which are formulated depending upon the vagaries of the market forces. Such cohesion and effectiveness are key to the success of any sales management organisational team.
We believe in serving our customers with the most reliable assignment help
Task 2: Understand the role and objectives of sales management
2.1 Explanation of how sales strategies are developed in line with corporate objectives
To achieve the intended growth strategy, the corporate entities work in several directions simultaneously. Sales strategies are generally constituted at management levels where the emphasis gets concentrated upon the market share possession, targeting of particular customers bases and positioning of the brand credentials of various products and services which the company such as the L’Oréal group offers. Usually the configurations of the cosmetic industry business units are oriented towards the application of the sales strategy implementation and to evaluate the market response from such endeavours. The sales strategies, regarding the product line of L’Oréal and other cosmetic production firms consider the approach methods to convince the customers from the point of view of grasping the greatest possible share of the existing market for cosmetic goods and to further expand on it (Johnstonet al. 2016, p.144). After the years of global recession, it is very interesting to observe that corporate concerns such as the L’Oréal group have begun to reconsider their strategy formulation to launch new and highly competitive brands into the markets. At the corporate levels, marketing strategies are considered as the as the functional strategies to be implemented at the market segments and business unit levels. The operational strategies, on the other hand are reserved to be utilised in the production phase levels for resource and cost appropriation (Hill et al.2014, p.127).
2.2 Explanation of the importance of recruitment and selection procedures
The importance of the recruitment and the selection process lies in the process of achievement of the organisational objectives of securing profitable market segments to ensure the survival and longevity of the product offerings. Any organization which operates in the modern competitive market scenario and provides consumption goods such as the biggest cosmetics and skin care substance producer, the L’Oréal group, requires to improve the organisational performance through the proper management of employees working in the organisation. This process demands the proper selection of the most suitable employees commensurate with the job profiles (Townley, 2014, p.92). The employee turnover rate and the attrition rate of employee loss get reduced if the propriety of the selection procedures involved in recruiting the potential workers could be optimised to select the best man for the designated job. Shortcomings in the selection of employees always lead to the improper performance of the business procedure and this contributes to financial loss for the relevant company. Proper and benefactor recruitment could be identified as the process of selecting the appropriate individuals for specific job profiles and encouraging them bring other similarly skilled personnel within the ambit of influence of the same organisations.
Stages of recruitment: Proper corporate recruitment consists of dual phased procedures. Firstly, the strategic planning process is operationalised to provide the specific delineation regarding the strategic objectives of the organisation. Secondly comes the next phase where the identification of the volume of necessary manpower is formalised. The objective of such corporate recruitment process is to attain the qualitative as well as the quantitative strength of the workforce that could become productive and fruitful within a short period of time and be assistive to the organization under which they are recruited to retain the competitive edge on the closest competitors in the market scenario (Breaugh, 2014, p.29).
2.3 Evaluate the role of motivation, remuneration and training in sales management
Role of motivation: Motivation is the key element in terms of retaining the operational edge of the employees and the overall human resource assets of the workforce. Motivation is the impetus which provides the enthusiasm in the employees of organisations such as the L’Oréal group which is of vital necessity for the performance enhancement requirement for the employees. Motivation makes the workers and the management personnel in any corporate organisation to take appropriate action regarding the entitled duty profiles that they are made responsible of. Motivation could be identified as the tool to achieve success in the sales management procedure through utilisation of the internal stimulus of the human nature to add value to the work that one performs inside the sales management team of any organisation (Kaplan and Atkinson, 2015, p.148).
Role of Remuneration in Sales Performance: Remuneration could be translated to the amount of direct monetary value that any employee or any group of employees could achieve as the result of the value of their work. The amount of money that is paid for the services rendered by the employees of the sales management groups is generally decided upon the explicit performance matrix of the employees and sales personnel in achieving the prescribed targets set down by the company (Pinder, 2014, p.132).
The proper management of remunerative incentives is vital to the direction of any sales and management teams and so is the case with the customer service team management as well. In any job profile description, the prospect of the availability of monetary incentives in a proportionate manner with that of the work performance exhibited is one of the enabling factors of adding quality to the performance of the employees. In terms of the sales team members, such incentives are generally subjects to the achievement of daily targets set by the corporate organisations.
Role of Training in Sales Performance:The term training denotes the process of acquisition of skills and capabilities and capacity enhancement through rigorous and time bound practice assisted by the training faculty of any organisation. It forms the basis of apprenticeships providing the groundwork of building skill sets in technical operations performed at the corporate sector. In addition to various basic training requirements to work in the corporate organisations such as the L’Oréal group observers and market researcher recognise the necessity of the continuous and persistent training schedules to better equip the working personnel with the variety of skill sets required to perform effectively in the modern hyper competitive working conditions where the constant need for performance improvement dominates the job profile of every employee (Guenziet al.2014, p.791).
2.4 Explanation how sales management organises sales activity and control sales output
Primarily, the basic techniques utilised to better coordinate and corroborate the sales efforts are oriented towards establishment of the product appeal in the imagination of the prospectus customers. These techniques could be broadly categorised into two segments as the sales output control method and the proper language utilisation (HÅ™ebíÄek et al.2014, p.103).
Sales output control: Such control processes are automatically and even manually activated in terms of the directives in the sales document. For the initialisation of the control process, the initial stage consists of the detailed study of the conditions delineated in the output measurement records. The question of whether is to implement such control processes or not completely depends upon the market conditions and the product life cycle.
Language: This could be identified as the criteria under which the output conditions are evaluated and maintained for automatic determination of output value. The documentation language of such organisational sales efforts offers the necessary flexibility of transforming the priorities in the annual sale statements regarding the profit ratios that had been set to be achieved prior to the issuing of such statements. Even in customer service control and to cater to customer specific needs, the documentation language becomes the key principle to achieve the required transformations (Ahearne et al.2013, p.636). For an instance, it could be highlighted that if any customer requires the ordered merchandise to be delivered within a definite time frame despite initially placing the order in a bulk processing batch, the commensurate changes could be introduced in the dispatch control mechanism to suit the new conditions and the sales orders could be thus updated to accommodate the changes as well.
2.5 Explain the use of databases in effective sales management
The proper utilisation of sales development software application and management of online sales promotion through specific database administration assist a sales manager to meet the presented challenges regarding sales team performance enhancement. Such database management also helps to end the sales lead spreadsheet disorganisation. The sales lead software compares and merges monthly sales leads from the sales team representatives. The application of the QuickBase data management contributes in tracking sales leads and simultaneously updates the adjoining data in the central database of the company(Mancini and Corsi, 2016, p.33).
Want to Join the Circles of
HIGH ACHIEERS?Make it a reality with our EXPERTS
Order NowTask 3
3.1 Identifying the lines choice and developing a sales plan
L’Oreal has recently launched its new lines for selling in both the international markets and in its domestic market. The new lines are: L’Oreal Bright Reveal Skincare, L’Oreal Revitalift Laser, L'Oreal Paris Revitalift Laser X3 Anti Aging Power Water, L'Oreal Paris Age 30+ Skin Perfect Cream SPF 21 PA+++, L’Oreal Studio, and so on. The sales plan of these new products will include the following strategies:
Market Segmentation:This depends on the extant market situation. As an example L'Oreal Paris Revitalift Laser X3 Anti Aging Power Water is priced Rs. 559 which may appear too much in a country like Bangladesh or India, but this may not be too much in the USA and France. So the prices of products need to vary from one market to another. Paris Age 30+ Skin Perfect Cream SPF 21 PA+++ is priced at Rs.119 that sounds little lower than the expected range and may well suit the developing markets. Demand is also another key feature here. L’Oreal may even go for a special penetration price that suits the targeted market. If the price of L’Oreal Bright Reveal Skincare seems a little higher than the average price, L’Oreal may go for a cut in its cost price and focus more on the number of products sold. The estimated sales and the trend of the sales are crucial as this will help project the real demand in the market (Kerzner, 2013, p.150).
Resource Development and allocation: It has to be based on the internal market audit. This will help plan the different aspects of the Sales plan: the human resource, training of that human resource, availability of the resource materials for production and the proper allocation of the products in the different markets as per requirement. If there is extra production, the amount of that has to be well calculated so that proper management of the extra amount can be done in time. For the management of the staff eligible consultants and managers are required. L’Oreal needs to focus on the allocation part as it does not have a strong network of salesman in the distant areas and the market penetration gets affected.
Advertising Strategy:L’Oreal may go for online strategies and tie-up with different companies like Google, e-Bay and so on. It may also use the social media as a tool for advertisement. This also includes the time and the medium of advertisement. L’Oreal may use the radio as it will have a greater reach in the developing countries and help increase the brand name. Television can be another good medium and this also includes the use of images. Advertisement in the newspapers can also be another important medium (Leigh and Blakely, 2013, p.121).
Marginal Cost analysis:Under this section the calculation of the extra products alongside the wages and the advertisement cost gone into it are calculated, and according to that the profit-loss estimate is done it is necessary for L’Oreal to calculate its marginal costs and the surplus value in time as it determines the sales price and advertisement costs.
3.2 Investigating opportunities for selling in the international market
As L’Oreal concentrates on different types of cosmetic products it needs to concentrate on specialization on different types of products such as skin care, hair-styling, eye cream and perfumeries. In the international markets especially in Asian markets the demand for creams that enhance fairness is increasing and L’Oreal should focus on the production of those creams at an affordable price. This also includes specialization on that type of product. As L’Oreal is the top brand in the world it gives them an advantage and they should utilize that. In 2015 skin care products market share was around 29.6% in the overall sales figure. Make-up took the second spot with 23.8%(approx) and hair care 19.7%. This also hints at the fact that the growing demand is for these products. Creams that slacken the symptoms of aging are going to be very effective in the European markets as the Continent has been facing a problem of Aging population. Diversifying the market will also help it know the different types of demand in the remote areas and disseminate its base (Heikkurinen and Bonnedahl, 2013, p.194).
3.3 Evaluating the role of trade fairs and exhibitions in selling
There are certain measures that a respective product can get maximum exposure through trade fairs and exhibitions. At a glance, a trade fair is a collection of business giants as well as customers. Some important roles of trade fairs and exhibitions are as follow:
Potential customer range: A business or product exhibition means gathering of business giants as well as targeted customers. In general exhibitions are managed for a specific business niche or industry. Therefore gathered customers can be referred as potential and a respective product marketing may gain true value as well as exposure to the right eyes (Tansu and Kaynak, 2013, p.137).
Opportunities of business trading: There are some products those are managed by business owners as well as individuals. For example, an exhibition regarding fairness or moisturising creame may gather professionals of parlours and some leading industry leaders. Therefore a product like L’Oréal may get additional attention of business heads. Besides that quality as well as review of products in an exhibition is supportive for making new marketing strategies as well as manufacturing expertise (Shani and Chalasani, 2013, p.123).
Business glances of competitors: A specific trade fair gathers different business heads under the same niche for exchanging products and these exchanges record value and quality standard of products. Following the same, a respective product can feel market competition and attention of targeted customers (Witt and Rao, 2015, p.394).
Resources of new marketing strategies: A closer view of the customers help find new marketing strategies. However, it is important to explore some expectations and feelings of customers while promoting a fairness cream in the market. Thus trade fairs are also supportive in terms of making new marketing strategies (Rinallo et al. 2016, p.143).
Conclusion
Therefore, it can be said that sales planning and promotion needs different dimensions of marketing as well as analysis of customer expectations. Practically, if a respective sales person gets unable to meet satisfactory measures of customers, there will be least outcome of all the efforts. In the above study, all of these prospects are better analysed along with an effective sales plan for a fairness cream product L’Oréal.
For more, visit Instant Assignment Help Australia
Reference List
- Ahearne, M., Haumann, T., Kraus, F. and Wieseke, J., 2013. It’sa matter of congruence: How interpersonal identification between sales managers and salespersons shapes sales success. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 41(6), pp.625-648..
- Armstrong, G., Adam, S., Denize, S. and Kotler, P., 2014. Principles of marketing. Pearson Australia.
- Boone, L.E. and Kurtz, D.L., 2013. Contemporary marketing. Cengage learning.
- Breaugh, J., 2014, July. Employee recruitment. In Meeting the Challenge of Human Resource Management: A Communication Perspective(p. 29). Routledge.
- East, R., Wright, M. and Vanhuele, M., 2013. Consumer behaviour: applications in marketing. Sage.
- Guenzi, P., Baldauf, A. and Panagopoulos, N.G., 2014. The influence of formal and informal sales controls on customer-directed selling behaviors and sales unit effectiveness. Industrial Marketing Management, 43(5), pp.786-800.
- Heikkurinen, P. and Bonnedahl, K.J., 2013. Corporate responsibility for sustainable development: a review and conceptual comparison of market-and stakeholder-oriented strategies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 43, pp.191-198.
- Hill, C.W., Jones, G.R. and Schilling, M.A., 2014. Strategic management: theory: an integrated approach. Cengage Learning.
- HÅ™ebíÄek, J., Soukopová, J., Štencl, M. and Trenz, O., 2014. Corporate key performance indicators for environmental management and reporting. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 59(2), pp.99-108.
- Hulthén, H., Hulthén, H., Näslund, D., Näslund, D., Norrman, A. and Norrman, A., 2016. Framework for measuring performance of the sales and operations planning process. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 46(9), pp.809-835.
- Ingram, T.N., LaForge, R.W., Avila, R.A., Schwepker Jr, C.H. and Williams, M.R., 2012. Sales management: Analysis and decision making. ME Sharpe.
- Jobber, D. and Lancaster, G., (2012), Selling and Sales Management, Pearson, London, 9th Edition.
- John, B., 2015. Consumer attitude and behaviour: A segmentational analysis. Journal of Research: THE BEDE ATHENAEUM, 6(1), pp.13-18.
- Johnston, M.W. and Marshall, G.W., 2016. Sales force management: Leadership, innovation, technology. Routledge.
- Kapferer, J.N., 2012. The new strategic brand management: Advanced insights and strategic thinking. Kogan page publishers.
- Kaplan, R.S. and Atkinson, A.A., 2015. Advanced management accounting. PHI Learning.
- Kerzner, H.R., 2013. Project management: a systems approach to planning, scheduling, and controlling. John Wiley & Sons.
- Kotler, P., Burton, S., Deans, K., Brown, L. and Armstrong, G., 2015. Marketing. Pearson Higher Education AU.
- Lassk, F.G., Ingram, T.N., Kraus, F. and Mascio, R.D., 2012. The future of sales training: Challenges and related research questions. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 32(1), pp.141-154.












